全文摘要
本文深入探讨了拖延症背后的科学原理,并提供了多种实用策略来克服拖延,提高生产力。文章首先定义了拖延症,并分析了其心理和行为原因。接着,提出了四种即时化奖励和后果、设计未来行动、使任务更易实现的方法来立即停止拖延。最后,讨论了如何通过建立日常习惯和使用视觉提示来持续避免拖延。
Procrastination is a challenge we have all faced at one point or another. For as long as humans have been around, we have been struggling with delaying, avoiding, and procrastinating on issues that matter to us.
During our more productive moments, when we temporarily figure out how to stop procrastinating, we feel satisfied and accomplished. Today, we’re going to talk about how to make those rare moments of productivity more routine. The purpose of this guide is to break down the science behind why we procrastinate, share proven frameworks you can use to beat procrastination, and cover useful strategies that will make it easier to take action.
You can click the links below to jump to a particular section or simply scroll down to read everything. At the end of this page, you’ll find a complete list of all the articles I have written on procrastination.
I. The Science Behind Procrastination
- What is Procrastination?
- Why Do We Procrastinate?
- The Procrastination-Action Line
II. How to Stop Procrastinating Right Now
- Make the Rewards of Taking Action More Immediate
- Make the Consequences of Procrastination More Immediate
- Design Your Future Actions
- Make the Task More Achievable
III. Being Consistent: How to Kick the Procrastination Habit
- The Daily Routine Experts Recommend for Peak Productivity
- How to Avoid Chronic Procrastination With Visual Cues
The Science Behind Procrastination
Let’s start by getting the basics nailed down. What is procrastination? What does procrastination mean? What exactly are we dealing with here?
What is Procrastination?
Human beings have been procrastinating for centuries. The problem is so timeless, in fact, that ancient Greek philosophers like Socrates and Aristotle developed a word to describe this type of behavior: Akrasia.
Akrasia is the state of acting against your better judgment. It is when you do one thing even though you know you should do something else. Loosely translated, you could say that akrasia is procrastination or a lack of self-control.
Here’s a modern definition:
Procrastination is the act of delaying or postponing a task or set of tasks. So, whether you refer to it as procrastination or akrasia or something else, it is the force that prevents you from following through on what you set out to do.
Why Do We Procrastinate?
Ok, definitions are great and all, but why do we procrastinate? What is going on in the brain that causes us to avoid the things we know we should be doing?
This is a good time to bring some science into our discussion. Behavioral psychology research has revealed a phenomenon called “time inconsistency,” which helps explain why procrastination seems to pull us in despite our good intentions. Time inconsistency refers to the tendency of the human brain to value immediate rewards more highly than future rewards.
The best way to understand this is by imagining that you have two selves: your Present Self and your Future Self. When you set goals for yourself — like losing weight or writing a book or learning a language — you are actually making plans for your Future Self. You are envisioning what you want your life to be like in the future. Researchers have found that when you think about your Future Self, it is quite easy for your brain to see the value in taking actions with long-term benefits. The Future Self values long-term rewards.
However, while the Future Self can set goals, only the Present Self can take action. When the time comes to make a decision, you are no longer making a choice for your Future Self. Now you are in the present moment, and your brain is thinking about the Present Self. Researchers have discovered that the Present Self really likes instant gratification, not long-term payoff.
So, the Present Self and the Future Self are often at odds with one another. The Future Self wants to be trim and fit, but the Present Self wants a donut. Sure, everyone knows you should eat healthy today to avoid being overweight in 10 years. But consequences like an increased risk for diabetes or heart failure are years away.
Similarly, many young people know that saving for retirement in their 20s and 30s is crucial, but the benefit of doing so is decades off. It is far easier for the Present Self to see the value in buying a new pair of shoes than in socking away $100 for 70-year-old you. (If you’re curious, there are some very good evolutionary reasons for why our brain values immediate rewards more highly than long-term rewards.)
This is one reason why you might go to bed feeling motivated to make a change in your life, but when you wake up you find yourself falling back into old patterns. Your brain values long-term benefits when they are in the future (tomorrow), but it values immediate gratification when it comes to the present moment (today).
The Procrastination-Action Line
You cannot rely on long-term consequences and rewards to motivate the Present Self. Instead, you have to find a way to move future rewards and punishments into the present moment. You have to make the future consequences become present consequences.
This is exactly what happens during the moment when we finally move beyond procrastination and take action. For example, let’s say you have a report to write. You’ve known about it for weeks and continued to put it off day after day. You experience a little bit of nagging pain and anxiety thinking about this paper you have to write, but not enough to do anything about it. Then, suddenly, the day before the deadline, the future consequences turn into present consequences, and you write that report hours before it is due. The pain of procrastinating finally escalated and you crossed the “Action Line.”
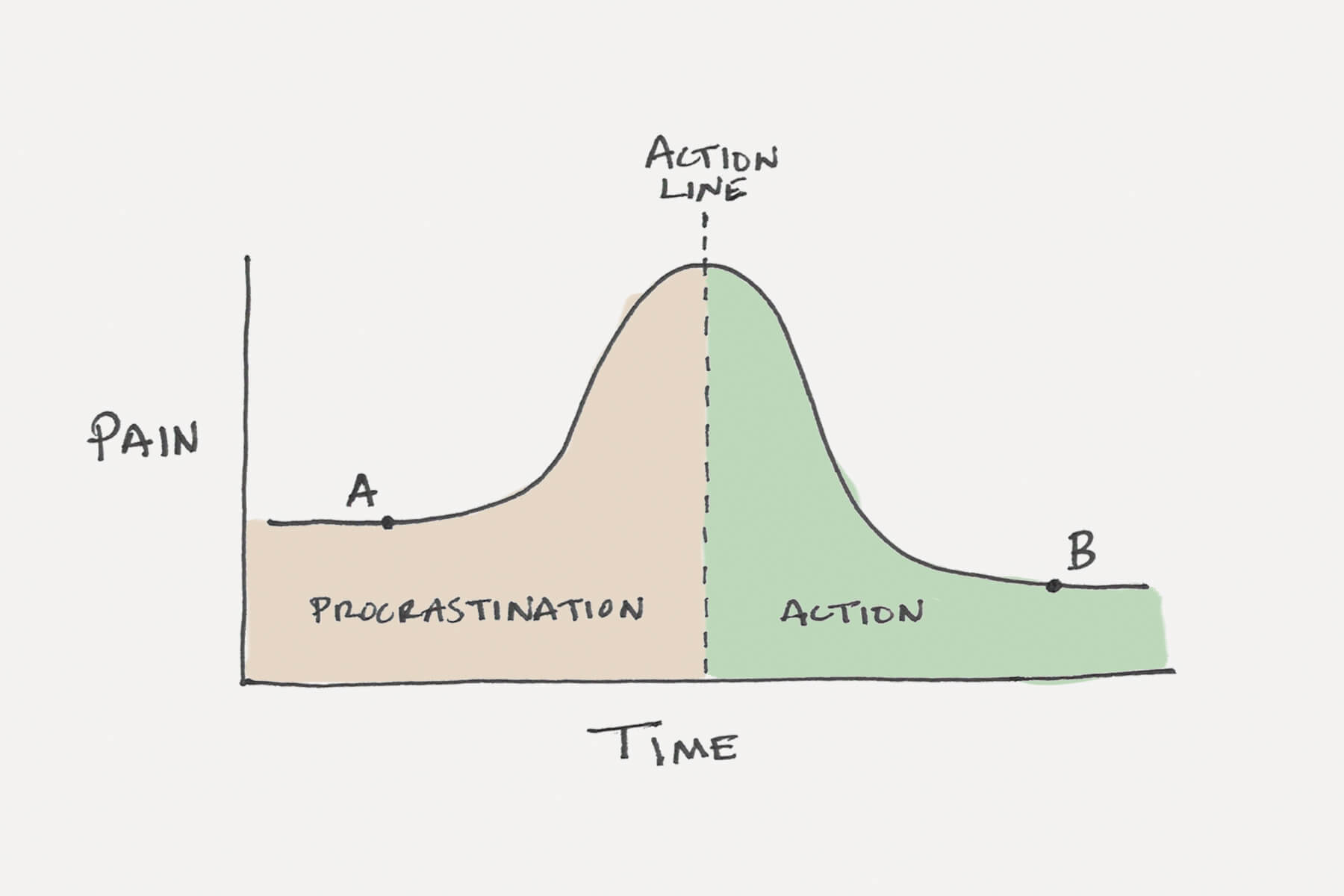
There is something important to note here. As soon as you cross the Action Line, the pain begins to subside. In fact, being in the middle of procrastination is often more painful than being in the middle of doing the work. Point A on the chart above is often more painful than Point B. The guilt, shame, and anxiety that you feel while procrastinating are usually worse than the effort and energy you have to put in while you’re working. The problem is not doing the work, it’s starting the work.
If we want to stop procrastinating, then we need to make it as easy as possible for the Present Self to get started and trust that motivation and momentum will come after we begin. (Motivation often comes after starting, not before.)
Let’s talk about how to do that now.
How to Stop Procrastinating Right Now
There are a variety of strategies we can employ to stop procrastinating. Below, I’ll outline and explain each concept, then I’ll provide you with some examples of strategy in action.
Option 1: Make the Rewards of Taking Action More Immediate
If you can find a way to make the benefits of long-term choices more immediate, then it becomes easier to avoid procrastination. One of the best ways to bring future rewards into the present moment is with a strategy known as temptation bundling.
Temptation bundling is a concept that came out of behavioral economics research performed by Katy Milkman at The University of Pennsylvania. Simply put, the strategy suggests that you bundle a behavior that is good for you in the long-run with a behavior that feels good in the short-run.
The basic format is: Only do [THING YOU LOVE] while doing [THING YOU PROCRASTINATE ON].
Here are a few common examples of temptation bundling:
- Only listen to audiobooks or podcasts you love while exercising.
- Only get a pedicure while processing overdue work emails.
- Only watch your favorite show while ironing or doing household chores.
- Only eat at your favorite restaurant when conducting your monthly meeting with a difficult colleague.
This article covers some specific exercises you can follow to figure out how to create temptation bundling ideas that work for you.
Option 2: Make the Consequences of Procrastination More Immediate
There are many ways to force you to pay the costs of procrastination sooner rather than later. For example, if you are exercising alone, skipping your workout next week won’t impact your life much at all. Your health won’t deteriorate immediately because you missed that one workout. The cost of procrastinating on exercise only becomes painful after weeks and months of lazy behavior. However, if you commit to working out with a friend at 7 a.m. next Monday, then the cost of skipping your workout becomes more immediate. Miss this one workout and you look like a jerk.
Another common strategy is to use a service like Stickk to place a bet. If you don’t do what you say you’ll do, then the money goes to a charity you hate. The idea here is to put some skin in the game and create a new consequence that happens if you don’t do the behavior right now.
Option 3: Design Your Future Actions
One of the favorite tools psychologists use to overcome procrastination is called a “commitment device.” Commitment devices can help you stop procrastinating by designing your future actions ahead of time.
For example, you can curb your future eating habits by purchasing food in individual packages rather than in the bulk size. You can stop wasting time on your phone by deleting games or social media apps. (You could also block them on your computer.)
Similarly, you can reduce the likelihood of mindless channel surfing by hiding your TV in a closet and only taking it out on big game days. You can voluntarily ask to be added to the banned list at casinos and online gambling sites to prevent future gambling sprees. You can build an emergency fund by setting up an automatic transfer of funds to your savings account. These are all examples of commitment devices that help reduce the odds of procrastination.
Option 4: Make the Task More Achievable
As we have already covered, the friction that causes procrastination is usually centered around starting a behavior. Once you begin, it’s often less painful to keep working. This is one good reason to reduce the size of your habits because if your habits are small and easy to start, then you will be less likely to procrastinate.
One of my favorite ways to make habits easier is to use The 2-Minute Rule, which states, “When you start a new habit, it should take less than two minutes to do.” The idea is to make it as easy as possible to get started and then trust that momentum will carry you further into the task after you begin. Once you start doing something, it’s easier to continue doing it. The 2–Minute Rule overcomes procrastination and laziness by making it so easy to start taking action that you can’t say no.
Another great way to make tasks more achievable is to break them down. For example, consider the remarkable productivity of the famous writer Anthony Trollope. He published 47 novels, 18 works of non-fiction, 12 short stories, 2 plays, and an assortment of articles and letters. How did he do it? Instead of measuring his progress based on the completion of chapters or books, Trollope measured his progress in 15-minute increments. He set a goal of 250 words every 15 minutes and he continued this pattern for three hours each day. This approach allowed him to enjoy feelings of satisfaction and accomplishment every 15 minutes while continuing to work on the large task of writing a book.
Making your tasks more achievable is important for two reasons.
- Small measures of progress help to maintain momentum over the long-run, which means you’re more likely to finish large tasks.
- The faster you complete a productive task, the more quickly your day develops an attitude of productivity and effectiveness.
I have found this second point, the speed with which you complete your first task of the day, to be of particular importance for overcoming procrastination and maintaining a high productive output day after day.
Being Consistent: How to Kick the Procrastination Habit
Alright, we’ve covered a variety of strategies for beating procrastination on a daily basis. Now, let’s discuss some ways to make productivity a long-term habit and prevent procrastination from creeping back into our lives.
The Daily Routine Experts Recommend for Peak Productivity
One reason it is so easy to slip back into procrastination time after time is because we don’t have a clear system for deciding what is important and what we should work on first. (This is yet another example of the system often being more important than the goal.)
One of the best productivity systems I have found is also one of the most simple. It’s called The Ivy Lee Method and it has six steps:
- At the end of each work day, write down the six most important things you need to accomplish tomorrow. Do not write down more than six tasks.
- Prioritize those six items in order of their true importance.
- When you arrive tomorrow, concentrate only on the first task. Work until the first task is finished before moving on to the second task.
- Approach the rest of your list in the same fashion. At the end of the day, move any unfinished items to a new list of six tasks for the following day.
- Repeat this process every working day.
Here’s what makes it so effective:
It’s simple enough to actually work. The primary critique of methods like this one is that they are too basic. They don’t account for all of the complexities and nuances of life. What happens if an emergency pops up? What about using the latest technology to our fullest advantage? In my experience, complexity is often a weakness because it makes it harder to get back on track. Yes, emergencies and unexpected distractions will arise. Ignore them as much as possible, deal with them when you must, and get back to your prioritized to-do list as soon as possible. Use simple rules to guide complex behavior.
It forces you to make tough decisions. I don’t believe there is anything magical about Lee’s number of six important tasks per day. It could just as easily be five tasks per day. However, I do think there is something magical about imposing limits upon yourself. I find that the single best thing to do when you have too many ideas (or when you’re overwhelmed by everything you need to get done) is to prune your ideas and trim away everything that isn’t absolutely necessary. Constraints can make you better. Lee’s method is similar to Warren Buffett’s 25-5 Rule, which requires you to focus on just five critical tasks and ignore everything else. Basically, if you commit to nothing, you’ll be distracted by everything.
It removes the friction of starting. The biggest hurdle to finishing most tasks is starting them. (Getting off the couch can be tough, but once you actually start running it is much easier to finish your workout.) Lee’s method forces you to decide on your first task the night before you go to work. This strategy has been incredibly useful for me: as a writer, I can waste three or four hours debating what I should write about on a given day. If I decide the night before, however, I can wake up and start writing immediately. It’s simple, but it works. In the beginning, getting started is just as important as succeeding at all.
It requires you to single-task. Modern society loves multi-tasking. The myth of multi-tasking is that being busy is synonymous with being better. The exact opposite is true. Having fewer priorities leads to better work. Study world-class experts in nearly any field—athletes, artists, scientists, teachers, CEOs—and you’ll discover one characteristic runs through all of them: focus. The reason is simple. You can’t be great at one task if you’re constantly dividing your time ten different ways. Mastery requires focus and consistency.
Regardless of what method you use, the bottom line is this: Do the most important thing first each day and let the momentum of the first task carry you into the next one.
How to Avoid Chronic Procrastination With Visual Cues

Another way to overcome the trap of chronic procrastination is to use visual cues to trigger your habits and measure your progress.
A visual cue is something you can see (a visual reminder) that prompts you to take action. Here’s why they are important for beating procrastination:
Visual cues remind you to start a behavior. We often lie to ourselves about our ability to remember to perform a new habit. ( “I’m going to start eating healthier. For real this time.” ) A few days later, however, the motivation fades and the busyness of life begins to take over again. Hoping you will simply remember to do a new habit is usually a recipe for failure. This is why a visual stimulus can be so useful. It is much easier to stick with good habits when your environment nudges you in the right direction.
Visual cues display your progress on a behavior. Everyone knows consistency is an essential component of success, but few people actually measure how consistent they are in real life. Having a visual cue—like a calendar that tracks your progress—avoids that pitfall because it is a built-in measuring system. One look at your calendar and you immediately have a measure of your progress.
Visual cues can have an additive effect on motivation. As the visual evidence of your progress mounts, it is natural to become more motivated to continue the habit. The more visual progress you see, the more motivated you will become to finish the task. There are a variety of popular behavioral economics studies that refer to this as the Endowed Progress Effect. Seeing your previous progress is a great way to trigger your next productive action.
Two of my favorite strategies that use visual cues are The Paper Clip Strategy, which is helpful for beating procrastination day-after-day, and The Seinfeld Strategy, which is great for maintaining consistency over longer periods of time.